Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-08 Origin: Site










Linear guides play a vital role in achieving precision motion in machinery. Have you ever wondered how machines maintain such accuracy and smooth movement? This article explores the different types of linear guides and helps you choose the best one for your needs. You’ll learn about the unique benefits of "Linear Guide With Flange Block" and its impact on various applications.
Linear guides are integral to ensuring precision and reliability in various mechanical systems. They are primarily used to guide loads along a predetermined path, which is essential for high-accuracy applications. By reducing friction, they enable smooth motion, thereby improving the overall efficiency and stability of machinery.
In CNC machines, 3D printers, and industrial robots, linear guides are critical in ensuring that the moving parts perform with high precision, which is essential for achieving desired outcomes in manufacturing and assembly tasks.

A linear guide system is composed of two primary elements: the rail and the block. The rail serves as the fixed component, while the block slides along the rail to provide movement. Inside the block, rolling elements such as steel balls or cylindrical rollers reduce friction and enhance motion efficiency. The smoother the interaction between the rail and the block, the more precise and stable the movement will be.
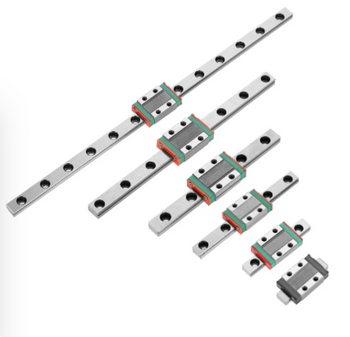
Linear guides can be classified into various categories based on their rolling elements, size, and structural design. The primary types include ball guides, roller guides, and miniature guides. Each type of guide is tailored to meet specific application needs, providing unique advantages depending on factors such as speed, load capacity, and environmental conditions.
Linear Guide Type | Rolling Element | Features | Best for Applications |
Linear Ball Guides | Steel Balls | Low friction, smooth motion, high-speed, low-load | CNC Machines, 3D Printers, Precision Measurement |
Linear Roller Guides | Cylindrical Rollers | High load-bearing capacity, high rigidity | Heavy-duty CNC Machines, Industrial Automation |
Miniature Linear Guides | Small Steel Balls or Rollers | Compact, high precision in small spaces | Laboratory Equipment, Precision Instruments, Small CNC |
Linear ball guides use steel balls as rolling elements, offering low friction and smooth motion. These guides are best suited for high-speed, low-load applications. The ball design allows for high precision and minimal energy loss, making them ideal for applications where fast movement and precision are essential.
● CNC machines
● 3D printers
● Precision measurement devices
Linear Guide With Flange Block: In ball guides, the addition of a flange block helps improve the installation stability and load capacity. The flange block design is particularly useful in high-precision applications where consistent alignment and strong support are required.
Tip: When working with high-precision machinery, "Linear Guide With Flange Block" models can enhance system stability, especially in applications that require consistent alignment under varying loads.
Linear roller guides replace steel balls with cylindrical rollers, which increases the guide's load-bearing capacity. This makes roller guides ideal for high-load, high-rigidity applications where ball guides would not suffice. The larger contact area between the rollers and the rail allows these guides to handle heavy-duty operations and resist deformation.
● Heavy-duty CNC machines
● Industrial automation
● Robotics
Roller guides excel in high-load applications where shock loads and long-term performance are crucial. They are especially suited for environments that require high rigidity, such as those found in large industrial systems.
Tip: Roller guides are highly recommended in environments with heavy shock loads or when rigidity is a top priority, such as in industrial robots or heavy-duty CNC machines.
Miniature linear guides are designed for compact spaces, making them ideal for applications with space constraints. These guides use small steel balls or rollers to provide precise motion in a small form factor. Despite their size, they maintain the core advantages of larger linear guides, such as low friction and smooth movement.
● Laboratory equipment
● Precision instruments
● Small CNC machines
● Optical equipment
The material selection for linear guides plays a significant role in their performance and longevity. The two most common materials used in linear guides are alloy steel and stainless steel, but other materials may be used depending on the application's specific needs.
Material | Characteristics | Best for Applications |
Alloy Steel | High rigidity, strong load-bearing capacity | High-precision, high-load industrial applications |
Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, performs well in humid or harsh conditions | Food Processing, Medical Equipment, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing |
Special Alloys | Customized for extreme environments | High-temperature, corrosive environments |
Alloy steel linear guides are known for their high rigidity and load-bearing capacity. They are suitable for industrial applications that require high precision and heavy-duty performance.
Stainless steel guides perform well in environments that are corrosive, humid, or dirty. This makes them perfect for industries like food processing, medical equipment, and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where durability and resistance to corrosion are essential.
Linear Guide With Flange Block: Stainless steel linear guides, especially with a flange block design, are widely used in environments subject to high temperatures or corrosive substances, offering enhanced durability and stability.
For applications in extreme environments, such as high temperatures or highly corrosive areas, special alloys are used to extend the service life of the guide while maintaining high precision. These materials are often custom-designed to ensure optimal performance under specific conditions.
When selecting a linear guide, the load capacity required for the application is a critical factor. If a system is expected to bear heavy loads, a roller guide or a heavy-duty ball guide is typically the best choice. For lighter loads, ball guides offer high-speed performance with sufficient precision.
Tip: Match the guide type to the load capacity required for your system. Roller guides are best for heavy loads, while ball guides are ideal for speed and lower loads.
Depending on the application's precision needs, you may choose between ball, roller, or miniature guides. Ball guides provide high precision for fine, intricate tasks, while roller guides are better suited for lower precision but higher load-bearing capacity.
Choose a linear guide based on environmental conditions. For example, stainless steel guides are ideal for humid or corrosive environments. Meanwhile, "Linear Guide With Flange Block" models offer superior stability, preventing contaminants from entering the system.
Preload refers to the slight pressure applied to the rolling elements inside the guide to improve rigidity and accuracy. Choosing the right preload class (light, medium, or heavy) will affect the performance and lifespan of the guide.
Linear guides are essential for maintaining high rigidity and precise positioning in CNC machining. They ensure that the tools remain stable during operation, reducing the risk of errors caused by guide deformation. In industrial automation, they provide reliable, smooth motion that improves production efficiency.
In 3D printers, the accuracy of the linear guide directly affects the precision of the print path. Accurate movement along the X, Y, and Z axes ensures that the 3D model is printed with precision. Similarly, laser cutting equipment benefits from high-precision linear guides to maintain the integrity of the cutting path.
Medical devices such as imaging diagnostic equipment and precision measuring instruments rely heavily on the accuracy and stability of linear guides. These guides ensure that critical measurements and scans are carried out with the utmost precision.
Choosing the wrong linear guide for the expected load can lead to premature wear, reduced precision, and system failure. Make sure to select a guide with the appropriate load-bearing capacity for your application.
Not considering environmental factors like humidity, temperature, or dust can shorten the lifespan of your linear guide. Stainless steel or sealed guides are recommended in harsh environments.
While price is an important factor, it should not be the sole consideration. Quality, durability, and long-term cost savings should be factored into the decision-making process to ensure that you choose the best linear guide for your application.
Choosing the right linear guide is crucial for the smooth operation of industrial equipment. The proper guide type, like "Linear Guide With Flange Block," can enhance both performance and durability. By selecting the right guide, you can significantly improve machinery efficiency and reduce maintenance costs. For tailored advice, consult experts at Shandong Yunfan Precision Bearing Co., Ltd. to find the best solution for your needs.
A: The main types of linear guides are ball guides, roller guides, and miniature guides. Each type has specific applications depending on load, speed, and precision requirements.
A: A "Linear Guide With Flange Block" is a linear guide system that includes a flange block, which helps improve installation stability and load capacity. It's ideal for high-precision applications where consistent alignment is crucial.
A: Linear roller guides use cylindrical rollers and are ideal for high-load, high-rigidity applications, while ball guides use steel balls and are better for high-speed, low-load applications.
A: A "Linear Guide With Flange Block" provides enhanced stability and improved load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-duty machinery and precision equipment.
A: Consider factors like load capacity, precision requirements, environmental conditions, and material compatibility. A "Linear Guide With Flange Block" is a good choice for applications needing high precision and stability.
A: Linear guides are widely used in industries such as CNC machining, 3D printing, medical equipment, and industrial automation due to their precision and load-bearing capabilities.
A: While "Linear Guide With Flange Block" models may cost more due to their enhanced stability and load capacity, they provide long-term value by improving equipment performance and reducing maintenance costs.
Copyright © 2023 Shandong Yunfan Precision Bearing Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Technology by leadong.com